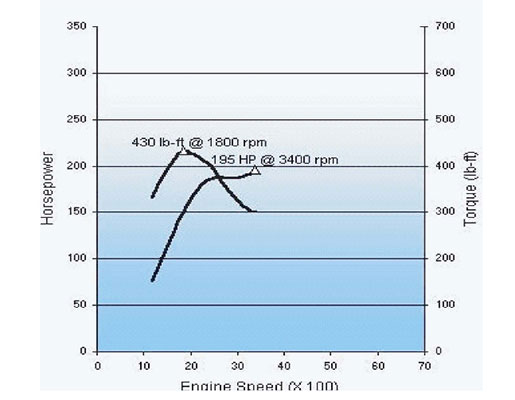
Acdc software free for windows 10. 6.5 Turbo Diesel Performance. 6.5 turbo diesel performance is one of the things that makes owning one so worth it. Not in stock form necessarily but with the ease of what amounts to bolt on mods. In stock form and in well maintained shape, the 6.5 can give reasonable performance for a daily driver or occasional hauling. I'm looking for the head torque spec for 6.5 turbo diesel with studs and nuts. Is there a certain way to torque these and do I add washers? Your help is appreciated. Type: 6.5L V8 Turbo Diesel Displacement: 6468 cc Compression Ratio: 19.5:1 Valve Configuration: Overhead Valves Manufactured: Moraine, OH Valve Lifters: Hydraulic Roller Firing Order: 1-8-7-2-6-5-4-3 Bore x Stroke: 103.00 x 97.03 mm Fuel System: Indirect Electronic Fuel Injection 215 hp @ 3400 rpm 195 hp @ 2600 rpm (C/K,G,P) Torque: 430 lb-ft @ 1800 rpm 430 lb-ft @ 1800 rpm (C/K automatic) 420. GM 6.5L-396ci-V8 Engine Torque Specs. Over 6,000 Automotive Torque Specs. Search Car Torque Specifications by Engine or Model.
- 6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Horsepower
- 6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Specifications
- 6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Chart
- 6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Diagram
| Hummer H1 | |
|---|---|
| Overview | |
| Manufacturer | AM General |
| Also called | Hummer HMC (1992–2002) HUMVEE C-Series (2017-current) |
| Production | 1992–2006 |
| Model years | 1992–2004, 2006 |
| Assembly | Mishawaka, Indiana, U.S. |
| Body and chassis | |
| Class | Large truck/SUV |
| Body style | 4-door Open Top - HMCO 4-door SUV - HMCS 4-door Hard Top - HMC4 2-door Fleet - KSC2 2-door Enlarged Cab - XLC2 |
| Layout | Front-mid engine, four-wheel drive |
| Related | Humvee military vehicle |
| Powertrain | |
| Engine | 6.2 L Detroit DieselV8 6.5 L Detroit DieselV8 5.7 L L05V8 6.5 L turbo Detroit DieselV8 6.6 L turbo DMAX DieselV8 |
| Transmission | GM TH400/3L80 3-speed automatic GM 4L80-E 4-speed automatic Allison 1000 5-speed automatic |
| Dimensions | |
| Wheelbase | 130 in (3,302 mm) |
| Length | 184.5 in (4,686 mm)[1] |
| Width | 86.5 in (2,197 mm) |
| Height | 77 in (1,956 mm) 2004–06: 79 in (2,007 mm) Pre-2003 Wagon: 75 in (1,905 mm) |
The Hummer H1 is a four-wheel-drive utility vehicle based on the M998 Humvee, which was created by AM General. The vehicle was produced from 1992 through 2006, and was the first of what became the Hummer line. Originally designed strictly for military use, the off-road vehicle was released to the civilian market due to market demand. It was initially known as the 'Hummer'; however, under a 1999 deal, GM bought marketing rights to the Hummer name and called the vehicle the Hummer H1.[2] At the time, GM began marketing the Hummer H2 that was also assembled by AM General on a modified GMC 2500HD chassis. AM General continued to build the H1 and Humvee in its Mishawaka, Indiana facility. GM stopped marketing the H1 in 2006 model year, but AM General continued production of the military Humvee versions.
6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Horsepower
History[edit]
Originally released in the civilian market March 14, 1992, the Hummer H1 became known from photographs published during Operation Desert Storm and the enthusiastic campaign from actor Arnold Schwarzenegger.
AM General announced that 2006 would be the last model year for the Hummer H1, with production winding down in June 2006 due to a new emission law for diesel engine vehicles, which took effect in 2007. The final model year of 2006 had the most powerful engine and improved fuel efficiency—about 10 mpg‑US (24 L/100 km; 12 mpg‑imp).[3]
Specifications[edit]
The Hummer H1 was available in three major variants: a convertible-like soft top, a four-door hard top Sport Utility Truck and an 'Alpha Wagon' body version. Less known variants were a two-door pickup truck and a four-door slantback, which shares the same body style of the Humvee employed by the U.S. Military. The convertible/soft top and the station SUV versions were the last types available to individual consumers.
Currently, five engine types and three automatic transmission types can be found in Hummer H1s. The common engine/automatic transmission combinations are:
- 6.2 L GM DieselV8/GM TH400/3L80 3-speed
- 6.5 L GM DieselV8/GM 4L80-E 4-speed
- 5.7 L (350 ci) L05 gasoline V8 TBI/GM 4L80-E 4-speed
- 6.5 L turbo GM DieselV8/GM 4L80-E 4-speed
- 6.6 L turbo Duramax LLYV8 turbo Diesel/Allison 1000 5-speed (model year 2006)
The Hummer H1 shares some common driveline parts with the HMMWV. These include brakes, axles, frame and major body panels (hood, tailgate and quarter panels) are shared between the HMMWV and Hummer H1. All H1s and HMMWVs were produced on the same assembly line; of which civilian H1s were then painted and finished in a separate building opposite the parking lot.
The H1 models are inherently stable due to their wide track. They can ford 30 inches (76 cm) of water and climb a 22-inch (56 cm) step. Their stock ground clearance of 16 inches (41 cm) is made possible by tucking driveline components inside a channel in the wide central space between the left and right seats. They have high approach/departure angles of 72/37.5 degrees. Most H1s are equipped with a Central Tire Inflation System (CTIS), which enables the driver to increase or decrease the tire air pressure at the push of a button, since lower tire pressures are more suited for off-road, and higher tire pressures are desirable on-road.[4]
Hummer H1s have other unusual features, such as inboard brakes and portal gears that allow the drivetrain's half shafts a higher placement, for greater ground clearance. The radiator is up high, sloping over the engine on a forward-hinged hood. The air intake is high-mount, enabling the H1 to ford waist-level water. Rather than using simple run-flat tire, magnesium-aluminum alloy or rubber inserts are an optional feature for runflat ability.[5] Options included leather seats, a winch kit, and running boards.[6]
2006 Hummer H1 Alpha[edit]
The 'Alpha' was an extensively re-engineered H1 that was equipped with GM's DuramaxDiesel and 5-speed Allison transmission. The previous turbo-diesel engine suffered from sluggish sales; lack of power was one of the reasons for customer resistance. In 2002, AM General CEO Jim Armour took the idea of repowering the H1 to Bob Lutz and the GM Luxury Vehicle committee. GM soon approved the use of their Duramax/Allison powertrain for the H1. This would support the continuation of the H1; it would also represent an updating in terms of power, torque, refinement and the ability to meet 2004 heavy duty EPA emissions requirements.
The update program commenced in late 2002 with production launch slated to be fall of 2004. The engineering team chose the engine variant out of the GMT560 truck (the C4500) because it packaged better into the H1 engine bay; however, 23 engine component changes were required and the team had to do a 2.0 in (51 mm) body lift to accommodate the taller engine and its turbo housing (a prior 0.5 in (13 mm) lift had been done for MY96 to accommodate the turbo on the 6.5L engine). The 8th digit of the VIN is 3, setting this version of the 6.6L Duramax apart from the versions used in pickup trucks.[7] The GMT560 engine calibration was used with minimal modification; engine output was 300 hp (220 kW) and 520 lb⋅ft (705 N⋅m) of torque. The Duramax engine was equipped with cooled exhaust gas recirculation and an internal engine oil cooler, thus, requiring a 40 percent heat rejection increase to engine coolant. Because space was limited between the air-lift brackets that protrude from the hood, the fan system was modified by putting it directly under the coolpack and driving it through a special gearbox directly off the crankshaft damper pulley. Several other cooling system modifications were required to assist with cold starting from −30 °F (−34 °C).
Other major modifications included the use of special high-strength steel in the chassis frame, a more powerful steering gear; quieter axle differentials, redesign of the geared hubs to use quieter helical gears, new induction, exhaust and electrical power systems; and re-engineering of the fuel supply and filtration system.
The Duramax engine delivered more torque at lower engine speeds than the 6.5L, combined with a lower gearing ratio (about 44.5 to 1 in low lock) made the vehicle more powerful. Other changes included centralized tire inflation and a new interior.
Production launch was early in 2005, and continued until production ceased in mid-2006. All vehicles built during this time are classified as model year 2006 (10th digit in VIN is a 6.)
The program was cancelled May 12, 2006 because GM decided to withdraw technical and financial support for future engineering and recertification.
The Hummer brand[edit]
On June 2, 2009, General Motors attempted a sale of its Hummer brand to a Chinese company, Tengzhong, as part of its bankruptcy settlement. GM stated at the time that it hoped the sale would save about 3,000 jobs in the US.
On February 24, 2010, General Motors announced that the company was shutting down its Hummer brand due to Tengzhong withdrawing its bid. Tengzhong stated that the bid was withdrawn due to a failure to get approval from the Chinese government.[8]
On January 30th, 2020, General Motors announced the revival of the Hummer nameplate, which would be used as a new electric off-road vehicle sub-brand within its GMC brand. The reborn Hummer, now known as the GMC Hummer EV, will have two variants, an SUV and a truck ('SUT'), with top variants reaching 1,000 hp from three electric motors.[9]
Yearly production[edit]
| Model year | Total production |
|---|---|
| 1992 | 316 |
| 1993 | 612 |
| 1994 | 718 |
| 1995 | 1,432 |
| 1996 | 1,374 |
| 1997 | 1,209 |
| 1998 | 945 |
| 1999 | 831 |
| 2000 | 1,333 |
| 2001 | 869 |
| 2002 | 704 |
| 2003 | 494 |
| 2004 | 252 |
| 2005 | 0 |
| 2006 | 729 |
| Total | 11,818 |
While there is no 2005 model year Hummer H1, the 2006 model year H1 Alphas were manufactured in both 2005 and 2006. 448 H1 Alphas were produced from January through May 2005, and 281 H1 Alphas were produced from September 2005 through May 2006, when the production for the Hummer H1 officially ended.[10]
Gallery[edit]
- Hummer H1 models
2004 Hummer undercarriage
A modified, red Hummer H1 in a parking lot
A Hummer H1 in Puerto Banús, a luxury marina in southern Spain
A camouflaged Humvee military version of hummer in San Francisco
A Hummer H1 Sport Utility Truck driving through mud and water
A Hummer H3, a Hummer H1, and a Hummer H2, showing the H1 in comparison to the other two models
- 1993 AM General Hummer H1 sales brochure
See also[edit]
- VLF Humvee C-Series and AM General Hummvee C-series kit cars – based on Hummer H1
6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Specifications
References[edit]
- ^Hummer. July 1999.
- ^'GM to discontinue original Hummer H1 model'. NBC News. Associated Press. May 12, 2006. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
- ^'Big, militaristic Hummer H1 on its way out'. USAToday. Associated Press. May 14, 2006. Retrieved May 22, 2017.
- ^'Hummer H1 Review'. Edmunds.com. Retrieved 2009-09-27.
- ^Hummer. July 1999.
- ^Hummer. July 1999.
- ^'Hummer H1 For Sale'. duPontREGISTRY. Retrieved 2017-01-13.
- ^G.M. to Close Hummer After Sale Fails
- ^Paukert, Chris. 'Hummer's electrifying return teased in GMC Super Bowl trailer'. Roadshow. Retrieved 2020-01-30.
- ^Hummer H1 2006 Model Year Changes, www.lynchhummer.com/Changes/h1.changes/06/2006.html
External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hummer H1. |
- Hummer H1 Maintenance Manuals Hummer H1 Maintenance Manuals and Parts
- Production Numbers - http://www.lynchhummer.com/Changes/h1.changes/production.numbers.html
Hummer, a division of General Motors, light truck timeline, 1992-2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | |||||||||||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 |
| SUV | H1 | H1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| H2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| H3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| SUT | H2 SUT | |||||||||||||||||||
| H3T |
Electronic fuel injection control system Both the normal (L56) and heavy-duty emissions certified (L65) versions of GM's turbo diesel engine utilize an electronic fuel-injection control system. This major technological enhancement incorporates a powertrain control module (PCM) that controls both the engine and transmission, an electronic throttle control and an electronically controlled fuel-injection pump. The adaptation of electronics to the rotary injection pump yields almost complete freedom to schedule fuel quantity and timing at optimal values for every speed and load point. What does all of this mean to the customer? Increased fuel economy, the elimination of black and white exhaust, improved cold weather starting, enhanced idle quality and reduced noise levels. The electronic fuel delivery system also helps protect the engine from overheating and other abuses, and allows GM to be fully compliant with current emissions standards. GM was the first manufacturer to introduce an electronically controlled fuel injection system in diesel pickup trucks.
6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Chart
The fuel injection pump was upgraded in 1997 and again in 1999 for improved durability by improving the Optical Sensor Tracking Encoder (OSTE) circuit board. In addition, the steel rollers in the pump were replaced with ceramic rollers for longer life. This system also makes available three electronically controlled Power Take Off (PTO) speeds. They are 1070 RPM, 1360 RPM, and 1600 RPM. These speeds can be activated by a simple switch.
Turbocharging When GM set out to design the 6.5L V8 diesel engine, the goal was to build an engine that was reliable and durable, with unparalleled performance. From the start, the 6.5L was designed specifically for turbocharging. The secret weapon behind the 6.5L turbo diesel is the GM computer controlled wastegate. This wastegate allows the turbocharger rotor speed and boost to be electronically adjusted as altitude and engine speed change, and as torque is needed. The wastegate helps the engine work harder, but only when it needs help. Mac os 7.6 download. When you need torque, it's there; when it's not required, the wastegate does not overwork the engine. The payoff is impressive fuel mileage, smooth, quiet operation and the necessary power to complete the job. This uniquely designed wastegate turbocharger delivers quick throttle response during acceleration and reduces turbo-boost pressure after obtaining maximum torque. The wastegate is designed to prolong turbo life and help manage the overall stress on internal engine components.
6.5 Turbo Diesel Engine Torque Specs Diagram
On-Board Diagnostics Second Generation (OBDII) As with all GM vehicles, GM's L56 and L65 turbo diesel engine is fully OBDII compliant. This required significant enhancements to the powertrain control module (PCM). The PCM, a highly sophisticated on-board computer, received a 50-percent increase in memory and improved diagnostic capabilities in 1996. The PCM, which began controlling the fuel-lift pump and air conditioner in 1996, also monitors sensor systems such as coolant temperature, fuel temperature, air temperature, barometer, exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) pressure, turbo boost pressure and the thermostat diagnostic. This technology will help GM vehicles meet the new, more stringent emissions regulations, as well as improve idle stability. Misfire detection was added to OBDII in 1998.
Turbocharging system On the G-van application of the L65, a center mounted turbocharging system shortens the air and oil passages and provides direct flow from the block. This design eliminates the need for oil lines, which increases reliability, durability, and serviceability. Oil is fed and drained directly from the block mount. Fuel-manager filter system Each of GM's diesel engines feature the fuel-manager filter system. This system is a double-filtration fuel filter that incorporates the filter, a water separator and a fuel heater all in one canister. The top-load vertical design and location simplify filter cartridge replacement.
Common serpentine accessory belt drive The 6.5L V8 diesel engine features a single serpentine belt for all the driven components. Its automatic tension adjuster improves belt life and makes servicing easier.
Fuel economy Among the many superior characteristics of the 6.5L turbo is its exceptional fuel economy. When matched against a comparably performing big-block V8 gasoline engine, this diesel has the potential for 25 to 80 percent better fuel economy. The improved fuel economy is a result of precise control of combustion and more precise transmission control, both due to electronic control.
Crankshaft bearings The crankshaft bearings used in the 6.5L are made of a fatigue-resistant material that promotes a higher bearing stress life. The rear crankshaft seal is in one piece to reduce the chances of leakage.
Boss health bar mod. Bulkhead The 6.5L diesel engine bulkhead area is designed to handle the higher-cylinder firing pressures of a turbocharged engine. In addition, the coolant passages and the oil galleries are sized to provide the increased flow required by a turbo engine.
Combustion chamber To provide smokeless performance and meet stringent emissions standards without sacrificing power, the 6.5L is designed with an optimized combustion chamber. This design provides an optimum balance of air in the prechamber, head and cylinder that ensures a more even and complete burning of fuel. For 1999 the compression ratio has been reduced to 19.5:1 and an exhaust pressure regulator system was added to eliminate white smoke.
Modulated exhaust gas recirculation system In addition to having an optimized precombustion chamber, the 6.5L L56 turbo engine utilizes an electronically controlled modulated exhaust gas recirculation system. This allows for more precise control over the flow of exhaust gas and also helps to meet stringent emissions standards.
Adaptive cylinder balance Adaptive cylinder balance is included on the 6.5L turbo diesel. This process measures the horsepower of each cylinder at idle and directs fuel to each cylinder accordingly. This results in smoother operation of the vehicle by minimizing the vibration of the engine.
Cylinder block The cylinder block incorporates piston spray cooling for increased engine life. This is accomplished by installing spray nozzles in the bulkhead that spray of oil at the underside of the piston. An increased flow oil pump and lubrication system ensure sufficient oil pressure during all running conditions. The oil cooler lines and oil coolers have increased in size so that they provide a 100% increase in flow through the oil cooler.
Cooling system The cooling system has been upgraded with an increased flow water pump and new water crossover and dual full-blocking thermostats. For 1999 the water pump bearing has been improved for greater durability.
Catalytic converter The catalytic converter was removed for 1999 while continuing to meet all emission requirements.
Oil pan capacity In 1999 the oil pan capacity increased to eight quarts, which reduces maintenance.

